DRI production
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) is the product of the direct reduction of iron – the removal of oxygen from iron ore or other iron bearing materials in the solid state, i.e. without melting, as in the blast furnace. The reducing agents are carbon monoxide and hydrogen, coming from reformed natural gas, syngas or coal. Iron ore is used mostly in pellet and/or lumpy form.
The chemical reactions involved in the direct reduction of iron are the following:
With H2
3Fe2O3 + H2 → 2Fe3O4 + H2O
Fe3O4 + H2 → 3 FeO + H2O
FeO + H2 → Fe + H2O
With CO
3Fe2O3 + CO →2Fe3O4 + CO
Fe3O4 + CO → 3 FeO + CO2
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
With solid carbon in reaction
CO2 + C → 2CO
Direct reduction processes
There are several processes for direct reduction of iron ore:
- gas-based shaft furnace processes Midrex® and Energiron being the main ones
– accounting for 75.8% of 2019 DRI production (total 108.1 million tonnes) - gas-based fluidized bed processes the Finmet / Finored process being the only commercial scale one in operation
– accounting for 0.2% of 2019 DRI production - coal based rotary kiln furnaces mainly in India
– accounting for 24% of 2019 production.
There are variants of these processes which are described on the websites of the various technology providers.
- Gas-based shaft furnace processes (2019) 75.8%
- Gas-based fluidized bed processes (2019) 0.2%
- Coal based rotary kiln furnaces (2019) 24%
DRI process types
Direct reduction process types
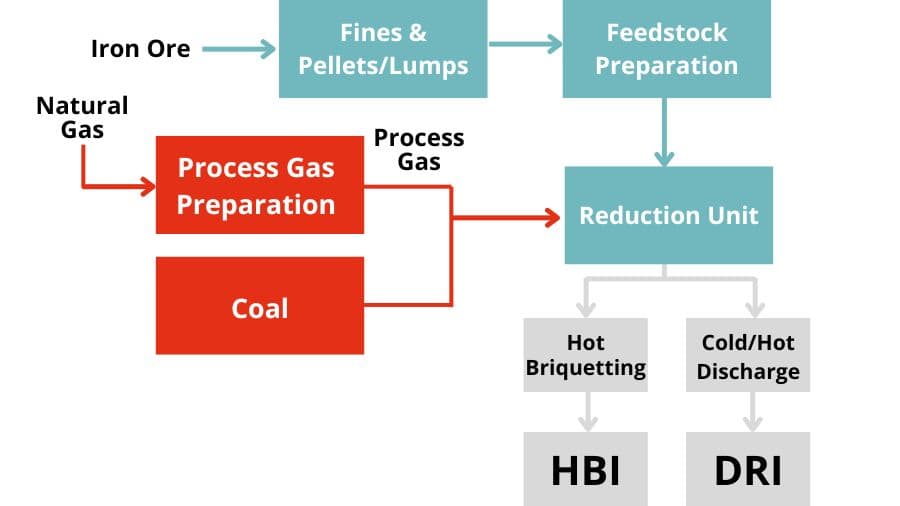

Direct reduction furnace types


Direct reduction processes for iron


DRI principal processes
The Midrex® and Energiron gas-based processes use predominantly iron ore pellets as feedstock, but sometimes with inclusion of lump ore in the furnace charge.




The Circored and Finmet / Finored gas-based processes utilize iron ore fines as feedstock.


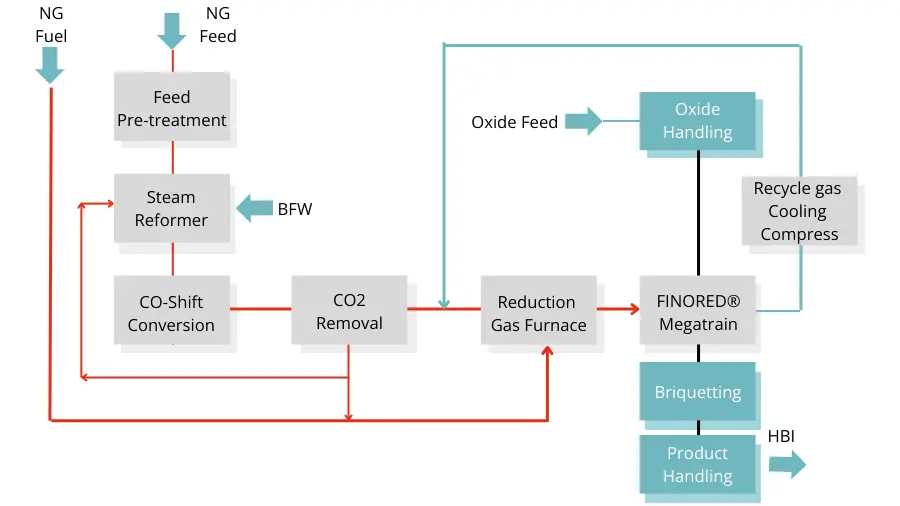

The SLRN coal-based rotary kiln process uses lump ore and, increasingly, pellets as feedstock.


More information on DRI
For further information about DRI see our DRI page or our fact sheet resources via the buttons below.
For answers to the most common technical questions on OBMs and their use and effects in different furnaces, see our OBM FAQs.
OBM production
Find out more information on how other OBMs are produced.
Fact sheets on ore-based metallics
Types of OBMs
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI)
DRI is the product of the direct reduction of iron ore in the solid state by carbon monoxide and hydrogen derived from natural gas or coal.
More about DRIHot Briquetted Iron (HBI)
HBI is a premium form of DRI that has been compacted at high temperature making it less reactive.
More about HBIPig Iron
Pig iron is the product of smelting iron ore (also ilmenite) with a high-carbon fuel and reductant such as coke, usually with limestone as a flux.
More about Pig IronGranulated Pig Iron (GPI)
Granulating excess pig iron produces a product GPI which can be used as BOF coolant or as feedstock for electric arc furnaces, cupolas and induction furnaces.
More about GPI











